Rubber spiral wound gaskets are designed to provide a highly effective seal by combining the strength of metal with the flexibility of rubber. This hybrid construction ensures that the gasket maintains a tight, durable seal even in high-pressure environments where traditional gaskets fail.
The metal windings contribute to the gasket’s mechanical strength, while the rubber fillers offer flexibility that allows the gasket to conform to flange irregularities, providing an optimal seal and preventing leaks.
These gaskets function in sealing high-pressure systems by preventing leaks in applications that require both mechanical strength and chemical resistance. According to a study by Popescu titled “Performance Analysis of Spiral Wound Gaskets for High-Pressure Sealing,” published in Engineering Journal (2023), rubber spiral wound gaskets can handle pressures up to 150 bar (2175 psi) while maintaining an effective seal, making them ideal for use in oil and gas and petrochemical industries.
The materials used in rubber spiral wound gaskets include a combination of stainless steel for the windings and rubber fillers such as EPDM or Viton, ensuring both chemical resistance and flexibility.
These gaskets are applied in chemical processing, nuclear energy, and marine applications. The installation process requires cleaning the flange surfaces and properly applying torque to ensure a tight seal. Proper installation maximizes the gasket’s performance by ensuring uniform compression and preventing seal failure due to misalignment.
What are Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Rubber spiral wound gaskets are sealing components designed to provide reliable and efficient sealing in industrial applications. These gaskets combine rubber’s flexibility and resilience with the structural strength of metal windings, ensuring durability and performance under extreme conditions.
Their primary purpose is to create leak-proof seals in flanged connections, particularly in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. The spiral wound gasket design allows them to adapt to flange irregularities while maintaining a tight seal, making them a preferred choice for sealing applications.
The key characteristics of rubber spiral wound gaskets include chemical resistance, thermal stability, and the ability to withstand significant mechanical stress, which is necessary for maintaining safety and efficiency in industrial operations.
What is The Design of Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The design of rubber spiral wound gaskets is characterized by a unique combination of metallic winding and filler material, engineered to provide both strength and adaptability.
The construction involves alternating layers of a V-shaped metal strip and a rubber-based filler, which work together to achieve a robust and flexible sealing solution.

The rubber spiral wound gasket design ensures excellent flexibility and compressibility, allowing the gasket to conform to flange irregularities and maintain a tight seal under varying pressure and temperature conditions.
The inclusion of a well-defined compression zone helps distribute sealing stress evenly across the flange surface, optimizing performance and preventing leaks.
Key design considerations for achieving optimal sealing performance include selecting materials that resist corrosion and degradation and ensuring durability and consistent sealing efficacy in demanding environments.
What Are The Dimensions Of Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Spiral wound gaskets are available in various dimensions, including diameters ranging from 0.5 inches (1.27 cm) to over 60 inches (152.4 cm). These dimensions cater to a wide range of applications, from small-scale piping systems to large industrial equipment.
The spiral wound gasket’s thickness varies between 3.2 mm (0.125 inches) and 7.2 mm (0.28 inches), depending on the required sealing performance and operating conditions.
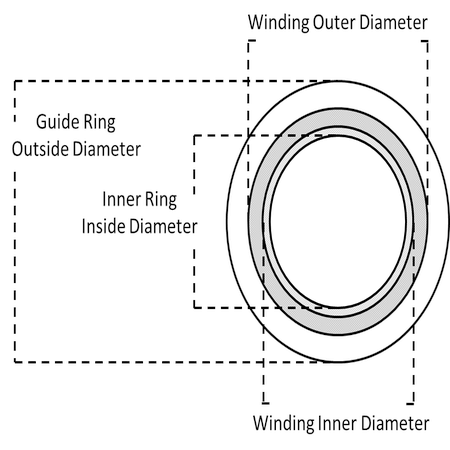
Specific types, such as Type RF1 and Type SG, are made for raised-face flanges, while Type RF IR and Type SG IR include inner rings for added reinforcement.
Type SG-RTJ provides increased sealing capability for ring-type joint applications. Specialized designs like Type HX-R and Type HX-RIR are engineered for high-pressure heat exchangers, ensuring optimal sealing under extreme conditions.
The selection of dimensions depends on flange specifications, pressure ratings, and the intended application’s temperature range.
How Are Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets Constructed?
Rubber spiral wound gaskets are constructed by winding a precisely shaped metal strip and inserting a rubber filler material in between. This combination of rubber-metal hybrid components ensures both structural strength and the flexibility required for effective sealing.
The metal winding strip provides durability and resistance to mechanical stress, while the rubber fillers accommodate surface irregularities and maintain a tight seal under varying operating conditions.
Material thickness and winding configuration play a massive role in sealing efficiency. For example, the thickness of the metal strip and the filler material is between 0.2 mm and 0.5 mm, depending on the gasket’s application requirements.
According to a study by Andrew V. Kearns titled “Improved Sealing Efficiency in Spiral Wound Gaskets for High-Pressure Systems,” published in Materials Science and Engineering (2022), spiral wound gaskets with enhanced graphite filler showed a 35% increase in sealing efficiency when exposed to extreme pressure and temperature conditions, maintaining leak prevention in industrial systems.
What Materials are Used for Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The materials used for rubber spiral wound gaskets include stainless steel for the winding strip and rubber fillers such as EPDM, NBR, or silicone. Optional inner and outer rings are made from carbon steel or other durable alloys to increase structural integrity and protect against damage during installation.
These material combinations ensure that the gaskets perform reliably under extreme pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure conditions.
The materials used for rubber spiral wound gaskets are explained below:
304 Stainless Steel
304 Stainless Steel is a commonly used material for the winding strip in rubber spiral wound gaskets, valued for its excellent corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and versatility in various environments.
This material withstands temperatures up to 870°C (1598°F) and resists oxidizing agents, making it suitable for general industrial applications. According to Popescu’s study, “Performance Analysis of Spiral Wound Gaskets for High-Pressure Sealing,” published in Engineering Journal (2023), 304 stainless steel is preferred for its cost-effectiveness and compatibility with a wide range of flanges.
316L Stainless Steel
316L Stainless Steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance compared to 304 due to its molybdenum content, making it ideal for environments with high chloride concentrations or exposure to aggressive chemicals.
It performs effectively in temperatures ranging from cryogenic levels to 800°C (1472°F). Its low carbon content also minimizes the risk of carbide precipitation, ensuring long-term reliability in corrosive conditions.
Monel
Monel, a nickel-copper alloy, is specifically used in applications requiring exceptional resistance to seawater, acids, and alkaline solutions. It maintains its structural integrity at temperatures up to 480°C (896°F).
According to a study by Alireza Farrokhi titled “Material Optimization for High-Stress Sealing Solutions,” published in Materials Science Review (2021), Monel gaskets are ideal for marine and petrochemical industries due to their excellent mechanical properties under extreme conditions.
PTFE
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is commonly used as a filler material in spiral wound gaskets due to its superior chemical inertness and temperature resistance. It operates reliably between -200°C (-328°F) and 260°C (500°F). PTFE is chosen for its low friction coefficient and ability to resist nearly all chemicals, ensuring sealing performance in highly reactive environments.
Non-Asbestos
Non-asbestos fillers are alternatives to traditional asbestos materials, offering similar heat resistance and sealing capabilities without the associated health risks. These materials include blends of aramid fibers and other synthetic components, suitable for temperatures up to 400°C (752°F). They are preferred in industries prioritizing safety and environmental compliance.
Viton
Viton is a high-performance fluoroelastomer that provides exceptional chemical resistance and withstands temperatures up to 205°C (401°F). Its durability in contact with fuels, oils, and aggressive solvents makes it an excellent choice for automotive and aerospace applications. The material also resists ozone and UV exposure, increasing its longevity in outdoor environments.
EPDM
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber is known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and aging, making it suitable for applications in steam and water systems. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C (-40°F) to 150°C (302°F). Its non-polar nature ensures compatibility with a wide range of fluids, including glycols and weak acids.
What Are the Properties of Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The main properties of rubber spiral wound gaskets include flexibility, pressure resistance, and chemical compatibility, making them a reliable choice for demanding sealing applications. Their ability to conform to irregular flange surfaces ensures a tight seal, even under fluctuating pressures and temperatures.
The use of materials like graphite-filled spiral-wound layers and elastomeric spiral seals improves their adaptability and resistance to wear.
These gaskets exhibit high compressibility, which allows them to recover from deformation caused by repeated loading, ensuring long-term sealing performance. Their excellent fatigue resistance also prevents failure in high-cycle applications.
The combination of these properties ensures durability and leak prevention, even in environments with aggressive chemicals or extreme thermal conditions, solidifying their role as versatile and dependable sealing components.
What Applications Do Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets Serve?
Rubber spiral wound gaskets are used in applications where high pressure and temperature resistance are needed, providing reliable sealing in precarious systems. They are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, petrochemical facilities, and pharmaceutical processing units.
According to a study by Guilherme F. M. Guimarães titled “Development and Experimental Validation of Leakage Models for Spiral-Wound Gaskets,” published in the Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering (2023), spiral wound gaskets with expanded graphite fillers demonstrate exceptional sealing performance in high-pressure chemical processing applications, ensuring tightness and resistance to corrosive agents.
In nuclear energy, these gaskets seal grave connections in reactors, resisting radiation and thermal degradation.
In marine systems, they maintain reliable seals in saltwater environments, preventing corrosion-related failures. Specific uses include sealing flanged connections in high-pressure vessels and reactors, ensuring leak-proof operations. Their robust design makes them suitable for handling steam, corrosive chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ensuring safety and efficiency.
How Do Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets Compare To Other Gasket Types?
Rubber spiral-wound gaskets compare with PTFE-filled spiral-wound gaskets and alternatives like cork, flat rubber gaskets, or solid metal gaskets in terms of their construction and superior sealing properties.
While PTFE or cork gaskets provide effective sealing in low-pressure and less demanding environments, rubber spiral wound gaskets excel in high-pressure applications due to their hybrid construction, combining a metallic winding with elastomeric spiral seals.
Compared to non-compressible seals or rigid metal seals, rubber spiral wound gaskets offer greater flexibility, enabling them to conform to irregular flange surfaces. The use of rubber fillers magnifies their chemical resistance, as they withstand aggressive chemicals and extreme thermal conditions.
For instance, PTFE-filled spiral-wound gaskets provide excellent chemical inertness but lack the compressibility and adaptability of rubber spiral-wound designs. Similarly, flat rubber gaskets are cost-effective but unsuitable for high-pressure environments due to their limited mechanical strength.
Rubber spiral wound gaskets’ multi-layered construction ensures that they maintain a reliable seal under fluctuating pressures and temperatures, making them indispensable for industrial applications demanding durability and performance.
What Industries Use Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Rubber spiral wound gaskets are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, automotive, and chemical processing, where their robust design ensures reliable, leak-proof seals in technical systems like pumps, valves, and pressure vessels.
According to a 2023 study by Jaszak and Adamek, titled “Design and Analysis of Flange-Bolted Joint with Respect to Tightness and Strength,” published in the Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, spiral wound gaskets significantly reduce leakage risks, maintaining operational integrity across various high-stakes industries.
Their ability to withstand high pressure and extreme temperatures makes them ideal for demanding applications in these sectors. In the oil and gas industry, these gaskets maintain the integrity of pipelines and flanged connections, handling pressures exceeding 150 bar (2175 psi) and temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F).
The marine industry relies on their corrosion resistance for sealing flanges in saltwater environments, while petrochemical plants benefit from their chemical compatibility in processing aggressive fluids.
In nuclear energy, rubber spiral wound gaskets are indispensable for sealing reactor components, ensuring safety under extreme thermal and radiation conditions.
What Are The Installation Procedures For Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The installation procedures of a rubber spiral wound gasket to ensure a secure seal are listed below:
- Clean the Flange Surfaces: Remove dirt, debris, and old gasket material to ensure a smooth, clean surface for the gasket to rest on.
- Position the Gasket: Align the gasket’s outer ring and inner ring with the flange to ensure proper placement.
- Apply the Appropriate Torque: Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten the bolts in a star pattern, evenly compressing the compression zone.
- Check for Leaks: After installation, pressurize the system and inspect for any potential leaks to confirm a proper seal.
Proper alignment and compression are necessary for achieving optimal sealing performance, as they prevent stress concentrations and uneven wear, which compromise the gasket’s integrity. According to Popescu’s study, “Performance Analysis of Flange Gaskets in High-Pressure Systems,” published in Engineering Journal (2023), correct installation reduces the risk of flange failures by 30% in high-pressure applications.
What Tools Are Needed For Installing Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Tools needed for installing rubber spiral wound gaskets include a torque wrench, gasket seating tools, and flange cleaning equipment. These tools ensure proper alignment, compression, and sealing performance, reducing the risk of leaks or gasket failure.
The tools needed for installing a rubber spiral wound gasket are:
- Torque Wrench: This tool ensures bolts are tightened to the precise torque specified by the manufacturer, preventing over-tightening that damages the gasket or causes uneven compression. Proper torque application is relevant for evenly sealing the compression zone.
- Gasket Seating Tools: Specialized tools such as centering rings or alignment pins help position the gasket accurately on the flange, ensuring that the outer ring and inner ring are correctly aligned to avoid leaks during operation.
- Flange Cleaning Equipment: Tools such as wire brushes, scrapers, and cleaning solvents are used to remove debris, old gasket material, and surface contaminants from the flange. Clean surfaces boost the gasket’s ability to form a tight seal and extend its lifespan.
It is better to use the torque value settings recommended by the gasket manufacturers to prevent flange distortion and over-tightening and ensure long-term sealing reliability. According to a study by Jaszak and Adamek, “Design and Analysis of Flange-Bolted Joint with Respect to Tightness and Strength,” published in the Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering (2023), improper torque application accounts for up to 40% of gasket failures in high-pressure systems.
What Mistakes Should Be Avoided When Installing Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Installation mistakes include over-tightening, misalignment, and failure to clean flange surfaces, all of which compromise the performance of flange gaskets. Following precise installation steps, such as using calibrated tools for exact torque settings, aligning the gasket accurately, and ensuring clean flange surfaces, is relevant for preventing leaks and prolonging the gasket lifespan.
The following are mistakes to avoid when installing rubber spiral wound gaskets:
- Over-Tightening: Excessive torque crushes the gasket, damaging the compression zone and reducing its ability to maintain a seal. Over-tightening contributes to flange gasket failures in high-pressure applications.
- Misalignment: Incorrect placement of the gasket relative to the flange prevents even sealing and exposes areas of the gasket to uneven stress, leading to leaks or gasket blowouts. Misalignment also weakens the flange gasket, particularly under thermal or pressure cycling.
- Failure to Clean Flange Surfaces: Dirt, debris, or remnants of previous gaskets create uneven surfaces, preventing the gasket from seating properly. This results in localized stress points and compromises the seal’s integrity, significantly reducing gasket performance.
How Does The Performance Of Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets Differ Across Applications?
The performance of rubber spiral wound gaskets can differ depending on factors such as material composition and application environment. In high-pressure settings, the design of high-temperature spiral-wound gaskets with materials like graphite or PTFE fillers ensures they withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses.
Temperature fluctuations and chemical exposure play significant roles; for instance, gaskets in chemical processing require materials resistant to corrosive agents, while those in steam applications need robust thermal stability.
Proper material selection is necessary to enhance the gasket’s lifespan and efficiency. For example, using metal windings combined with chemically inert fillers improves durability and prevents leakage in aggressive environments.
As sealing components in industries like oil and gas or nuclear energy, these gaskets maintain performance through optimized material and design configurations tuned to their specific applications.
What Factors Affect The Performance Of Rubber Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The performance of rubber spiral wound gaskets is influenced by the factors below:
- Material properties
- Installation technique
- Operating conditions
- Flange surface preparation
- Bolt tightening sequence
- Gasket design and thickness
- Pressure fluctuations
- Thermal cycling
Material Properties
Material Properties refer to the composition and quality of the metal windings and rubber fillers in the gasket. High-quality materials improve pressure resistance, chemical compatibility, and durability. According to a study by Guilherme F. M. Guimarães titled “Development and Experimental Validation of Leakage Models for Spiral-Wound Gaskets,” published in Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering (2023), selecting appropriate materials can extend gasket lifespan in aggressive chemical environments.
Pressure Resistance
Pressure Resistance is the ability of the gasket to maintain a seal under high-pressure conditions. Excessive pressure deforms the compression zone, compromising sealing efficiency. Gaskets designed for high-pressure applications handle up to 150 bar (2175 psi), ensuring operational integrity in systems such as oil pipelines.
Temperature
Temperature fluctuations, especially extreme heat or cold, degrade gasket materials and reduce their elasticity. High-temperature gaskets with graphite fillers perform reliably in environments exceeding 600°C (1112°F), while rubber fillers like EPDM are suited for moderate temperatures. Thermal cycling accelerates wear if the gasket is not designed for such conditions.
Chemical Exposure
Chemical Exposure affects the gasket’s resistance to corrosion and degradation. In petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries, exposure to aggressive chemicals weakens rubber fillers. PTFE-filled spiral-wound gaskets are particularly effective, as they resist most chemicals while maintaining their sealing properties.
Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure gasket performance, as worn or degraded gaskets lead to leaks and system failures. Proper monitoring helps detect issues early, reducing downtime and operational risks.
What Are The Different Types Of Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Spiral wound gaskets come in several types, including Type RF1, Type SG, Type RF IR, Type SG IR, Type SG-RTJ, Type HX-R, and Type HX-RIR, each designed for specific applications.
Type RF1 is commonly used for raised-face flanges, providing dependable sealing for moderate pressure and temperature conditions. Type SG is a versatile option suitable for a wide range of industrial applications due to its flexibility and adaptability.

Type RF IR builds on the RF1 design by adding an inner ring, enhancing structural reinforcement and sealing performance under high stress. Type SG IR features an inner ring like RF IR but is specifically designed for applications requiring exceptional pressure resistance.
Type SG-RTJ combines the spiral wound gasket’s adaptability with a ring-type joint configuration, making it ideal for oil and gas pipelines. Type HX-R is engineered for heat exchangers, performing effectively under high temperatures and cyclical thermal stress.
The HX-RIR variation includes an inner ring for enhanced sealing in extreme heat exchanger conditions, ensuring superior reliability in demanding environments. These premium rubber gaskets all excel in their different applications.
What Is The Specification For Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Spiral-wound gaskets have specific specifications related to material composition, thickness, temperature tolerance, and pressure ratings. They are constructed using a combination of metal windings and filler materials, such as graphite or PTFE, adapted to the application’s requirements.
Thickness specifications range from 3.2 mm to 7.2 mm, depending on the sealing performance needed for the flange configuration. Temperature tolerance for spiral wound gaskets varies based on the filler material and metal used.
For example, graphite-filled gaskets withstand temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F), while PTFE-filled gaskets perform effectively at lower maximum temperatures of approximately 260°C (500°F).
Pressure ratings also depend on the gasket’s design and materials, with many standard configurations supporting pressures up to 150 bar (2175 psi). Spiral wound gasket specifications ensure reliable sealing performance across diverse industrial applications, including oil and gas, petrochemical, and nuclear energy.
What Is The Difference Between CG And CGI Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The primary difference between CG and CGI spiral wound gaskets lies in the addition of an inner ring in CGI gaskets. The CG type consists of a spiral-wound core with an outer guide ring, primarily providing centering support and assisting in compression alignment during installation.

CGI gaskets, on the other hand, include both an outer guide ring and an inner ring. The inner ring enhances performance by increasing axial rigidity, protecting against extreme temperature variations, and preventing inward buckling during compression. This additional feature makes CGI gaskets more suitable for high-pressure and temperature applications compared to CG gaskets.
According to a study by Przemysław Jaszak and Konrad Adamek titled “Design method of enhancing the tightness of a spiral wound gasket with PTFE filling,” published in the Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering (2023), the inner ring in CGI gaskets provides a significant increase in structural stability and sealing performance by reducing deformation under high contact stresses.
Who Are the Leading Manufacturers of Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Leading manufacturers of spiral wound gaskets include Flexitallic, Garlock, Lamons, Mercer Gasket & Shim, and Technetics Group. These companies contribute significantly to the industry by delivering high-quality sealing components that ensure safety and efficiency in touch-and-go applications.
The leading manufacturers of spiral wound gaskets are:
- Flexitallic: A pioneer in the gasket industry, Flexitallic is credited with inventing the spiral wound gasket in 1912. The company has continued to innovate with products like the Change™ Gasket, designed for superior dynamic recovery and sealing efficiency. Flexitallic serves industries including petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and oil and gas, offering custom solutions for high-priority applications.
- Sigma®: Known for its high-performance gaskets, Sigma® offers specialized solutions for applications requiring high chemical resistance and sealing integrity. Its products are widely used in the pharmaceutical and chemical processing sectors.
- Dobson Gaskets: This manufacturer focuses on custom gasket solutions, including spiral wound gaskets designed to meet the needs of diverse industries. Dobson Gaskets insists on precision engineering and material quality for applications in nuclear energy and marine systems.
- Technetics Group: Technetics produces VITAFLEX® Spiral Wound Gaskets, which are engineered for extreme environments. Their gaskets are recognized for their reliability and performance in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, particularly in the oil and gas and chemical processing sectors.
- Lamons: A key supplier of sealing solutions, Lamons specializes in spiral wound gaskets for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Their products are widely used in petrochemical plants, refineries, and industrial applications requiring robust sealing solutions.
These gasket manufacturers offer advanced technologies and high-quality products that meet the unique demands of high-priority sealing applications.
What Is The Function Of The Inner Ring In Spiral Wound Gaskets?
The inner ring in spiral wound gaskets serves to increase gasket stability and sealing performance by providing additional structural support. Positioned on the inside edge of the winding material, it prevents inward buckling of the gasket during compression, ensuring a uniform and reliable seal across the flange. This feature is particularly relevant in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
The inner ring acts as a barrier, protecting the winding material and filler (such as graphite or PTFE) from chemical or mechanical damage caused by exposure to the system’s contents. It also helps distribute the compressive force evenly, reducing the likelihood of flange distortion or gasket failure.
As part of sealing components, the inner ring ensures the mechanical integrity of the assembly, enabling the gasket to maintain its performance over extended operating cycles.
What Is The Role Of Gasket Fillers In Spiral Wound Gaskets?
Gasket fillers, such as rubber or graphite, are essential in spiral wound gaskets because they provide flexibility, compressibility, and enhanced sealing ability. These fillers help the gasket conform to flange irregularities, ensuring a tight seal under varying pressure and temperature conditions.
Fillers like PTFE and graphite are commonly used for their chemical resistance, while mica and non-asbestos materials are preferred for high-temperature applications. Fillers contribute significantly to the gasket’s performance by maintaining its elasticity and sealing capacity over time, even under extreme conditions.
According to Popescu’s study (2023), spiral wound gaskets using graphite fillers improved sealing efficiency significantly compared to those using only metal windings, showing the importance of selecting the right filler material for optimal gasket performance.
How Do Spiral Wound Gaskets Perform Under Extreme Conditions?
Spiral wound gaskets are designed to withstand extreme conditions, including high temperature, high pressure, and chemical exposure. Their unique construction, which combines metal windings with flexible fillers such as graphite or non-asbestos materials, allows them to maintain a reliable seal in demanding environments.
For example, gaskets with 316L stainless steel windings offer excellent corrosion resistance and are ideal for high-temperature applications, performing effectively up to 800°C (1472°F).
In extremely high-pressure environments, such as those found in oil and gas pipelines, Inconel 600-based spiral wound gaskets ensure stability and sealing integrity, resisting deformation under pressures exceeding 200 bar (2900 psi).
The rubber spiral wound gasket’s combination of graphite fillers and 316L stainless steel provides optimal sealing performance. Graphite increases chemical resistance, while 316L stainless steel gives mechanical strength.
This configuration enables spiral wound gaskets to withstand harsh chemical environments, including aggressive acids and hydrocarbons, maintaining their sealing capability over extended periods.
What Are the Advantages of Spiral Wound Metal Gaskets?
Spiral wound metal gaskets offer significant advantages, including exceptional durability, flexibility, and high-pressure resistance. Their multi-layered design, combining metal windings and flexible filler materials, allows them to adapt to irregular flange surfaces, ensuring a tight, leak-proof seal.
This layered design also enhances sealing performance, as the compression zone is evenly distributed, preventing deformation under pressure.
The use of materials like 316L stainless steel and Inconel in the windings provides the spiral wound metal gaskets with the strength required for high-pressure applications, such as those found in the oil and gas and petrochemical industries.
Furthermore, the integration of spiral sealing rings or rubber seals ensures enhanced mechanical stability, making them ideal for use in mechanical seals under extreme operating conditions. The combination of these features makes spiral-wound metal gaskets a reliable solution for demanding industrial sealing applications.





