Rubber EPDM gaskets, made from ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, offer exceptional durability and resilience. They are ideal for environments requiring reliable sealing and provide a weather-resistant solution that prevents leaks and ensures long-lasting performance across various industrial applications.
The properties of rubber EPDM gaskets include excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperature fluctuations. These UV-resistant gaskets perform well in harsh outdoor conditions, making them ideal for sealing applications exposed to sunlight and environmental stress. EPDM exhibits flexibility and superior aging resistance, ensuring their longevity in demanding environments.
EPDM gaskets are widely utilized in various industrial applications, including automotive, construction, marine, and food processing sectors. These weather-resistant seals are important for applications requiring airtight and waterproof solutions, such as window seals, HVAC systems, and plumbing. They ensure optimal performance in high-stress environments, maintaining the integrity of mechanical systems and preventing leaks.
The manufacturing and installation process of EPDM gaskets involves techniques such as die-cutting, molding, and waterjet cutting, depending on the required specifications. These methods ensure precision in size and shape, allowing the gaskets to fit seamlessly into their designated applications. Proper installation is also needed, requiring careful surface preparation, correct alignment, and proper compression to ensure leak-free sealing.
The advantages of rubber EPDM gaskets lie in their cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatility. They offer a long-lasting, low-maintenance sealing solution for various industries. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, and weather conditions makes them a preferred choice for high-performance sealing components, providing reliable, long-term protection against leaks and environmental damage.
What are Rubber EPDM Gaskets?
Rubber EPDM gaskets are elastomeric seals made from ethylene-propylene-diene monomer, designed to prevent leaks and ensure long-lasting performance in harsh environments. These gaskets are integral to applications requiring robust sealing solutions, particularly in environments where exposure to harsh weather, chemicals, or mechanical stress is common.
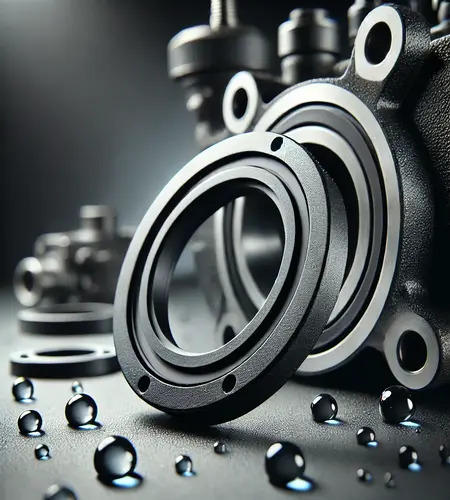

EPDM rubber seals prevent leaks and ensure structural integrity and long-lasting performance in various industrial, automotive, and construction settings. Their flexibility and resilience make them ideal for sealing irregular surfaces, accommodating movement, and maintaining a tight barrier under fluctuating conditions.
One of the standout features of EPDM rubber gaskets is their resistance to environmental degradation. As UV-resistant gaskets, they maintain their properties even after prolonged exposure to sunlight, making them well-suited for outdoor applications. Their ability to resist ozone cracking ensures longevity in conditions with high ozone concentrations, such as urban and industrial areas.
The weatherproof components of rubber EPDM gaskets remain unaffected by extreme temperatures, performing effectively in a range from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F). This resistance to thermal fluctuations makes them reliable in both freezing and high-heat scenarios, as studied by Basu D. et al., 2015, in their paper “Fire-Safe and Environmentally Friendly Nanocomposites Based on Layered Double Hydroxides and Ethylene Propylene Diene Elastomer.”
Beyond temperature and weather resistance, EPDM elastomeric gaskets show impressive chemical inertness, particularly against polar substances such as water, alcohol, and certain acids. This property ensures their performance in applications involving water-tight seals, such as plumbing systems, HVAC units, and automotive weatherstripping.
What are the Properties of Rubber EPDM Gaskets?
The properties of rubber EPDM gaskets are chemical resistance, durability, and temperature range tolerance. They excel in resisting polar chemicals, ensuring longevity in diverse industrial and environmental conditions. Their high durability, supported by excellent tear resistance, allows them to withstand mechanical stress without degradation. Their broad temperature range tolerance (-40°C to +120°C) ensures reliable performance in extreme cold and heat, making them a versatile choice for demanding sealing applications.

Below are the key properties of rubber EPDM gaskets:
- Tensile Strength and Flexibility: EPDM rubber gaskets exhibit impressive tensile strength, ranging from 7 MPa to 25 MPa, depending on the formulation and manufacturing process, as studied by Elastomer Research Testing. This ensures they endure mechanical stress while maintaining flexibility, which is necessary for applications requiring tight seals under dynamic conditions.
- Chemical Resistance: EPDM rubber gaskets are highly resistant to polar substances such as water, alcohol, and glycols, as well as weak acids and alkalis. This resistance is attributed to the saturated polymer backbone of EPDM, which inhibits chemical degradation, making them ideal for plumbing, HVAC, and industrial applications.
- Durability and Tear Resistance: EPDM rubber gaskets are known for their exceptional durability, demonstrating a tear resistance of approximately 9–17 kN/m, depending on the grade, according to the material testing standards such as ASTM D624 (Standard Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers). This robustness ensures longevity in environments subjected to mechanical wear and stress.
- Temperature Range Tolerance: EPDM rubber gaskets have a working temperature range of -40°C to +120°C (-40°F to 248°F), which is effective in extreme cold and high-heat conditions, according to a study by Bronowski D et al. 2000, titled “Performance testing of elastomeric seal materials under low and high-temperature conditions: Final report.” Improved formulations extend this range, making them suitable for both arctic and tropical applications.
- Weather Resistance: EPDM rubber gaskets are exceptionally resistant to UV radiation, ozone, and oxidation. A study by Costa NL et al. 2024, titled “A Review of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Rubber-Based Nanocomposites: Properties and Progress,” shows that these materials retain their elasticity and strength even after prolonged exposure to sunlight and atmospheric conditions, making them ideal weather-resistant components for outdoor applications.
How Do EPDM Gaskets Compare to Other Materials?
EPDM gaskets compare to other materials by offering superior weather, ozone, and UV resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Compared to other rubber types, EPDM is a reliable choice for environments that demand high durability and resilience under fluctuating temperatures and harsh conditions.
In Neoprene vs EPDM, EPDM excels in weather and UV resistance, whereas Neoprene degrades over time due to prolonged exposure to sunlight and ozone. Neoprene offers better oil and fuel resistance, and EPDM’s chemical stability against polar substances like water and steam makes it more suitable for plumbing and HVAC systems.
Silicone alternatives tolerate a broader temperature range, withstanding extreme heat up to +200°C, but EPDM surpasses them in mechanical toughness and abrasion resistance. This superior durability ensures EPDM’s reliability in applications involving constant mechanical stress and harsh environmental conditions.
EPDM is more cost-effective. It delivers excellent weatherproofing and resilience without the higher costs associated with Silicone, making it ideal for demanding industrial and outdoor uses.
Nitrile rubber, known for its superior oil resistance, is less effective in weatherproofing and ozone resistance than EPDM. This makes EPDM the preferred material for automotive weather stripping, roofing systems, and other outdoor applications where weather resistance is necessary.
EPDM is a robust rubber type because of its unique classifications, properties, and applications. It is an excellent choice for industries that demand durable and reliable sealing solutions.
What Applications Use Rubber EPDM Gaskets?
The applications that use rubber EPDM gaskets include automotive, construction, and marine seals due to their exceptional resistance to environmental stress, including UV exposure, ozone, and extreme temperatures. These properties make them indispensable in diverse applications requiring reliable and long-lasting sealing solutions.
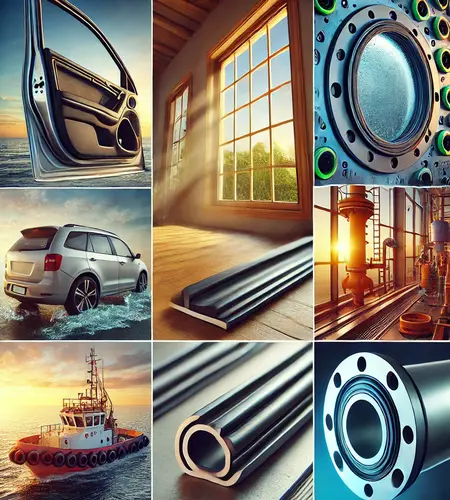

The applications that use rubber EPDM gaskets are as follows:
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive industry, EPDM gaskets are integral to weatherstripping for doors, windows, and trunk seals, protecting water, dust, and wind. For example, modern automotive weatherstripping uses EPDM due to its ability to maintain elasticity across a wide temperature range (-40°C to +120°C). A study by Im H, Jeoung S., et al. 2023, titled “Mechanical Aging Test and Sealing Performance of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate as Sealing Gasket in Automotive Fuel Cell Applications,” has shown EPDM’s durability in automotive seals exceeds 10 years under standard operating conditions, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Construction: EPDM gaskets are used in construction, roofing membranes, window glazing, and building insulation. They provide excellent thermal and weatherproofing performance, which is important for energy-efficient buildings. EPDM roofing membranes, for instance, are designed to last over 50 years with minimal maintenance due to their superior UV and ozone resistance, as validated by ASTM D4637 testing standards.
- Marine Seals: For marine seals, EPDM gaskets are important in sealing hatches, windows, and doors on boats and ships. Their resistance to saltwater, UV radiation, and harsh marine environments ensures reliability in preventing leaks and corrosion. EPDM’s low compression set (<15%) allows it to maintain its sealing integrity even after repeated stress, making it a preferred material for marine applications.
- Industrial Sealing: EPDM gaskets also benefit industrial sealing applications, particularly HVAC systems, pipelines, and machinery. Their resistance to polar substances like water and steam, combined with excellent flexibility, ensures a tight and durable seal under variable pressure and temperature conditions.
How Are Rubber EPDM Gaskets Manufactured?
Rubber EPDM gaskets are manufactured by molding, extrusion, and die-cutting, with each process tailored to achieve specific shapes, dimensions, and properties for various applications. These precision techniques ensure consistency and reliability in producing both solid and sponge rubber gaskets, depending on the application requirements.
Below are the primary ways EPDM gaskets can be manufactured:
Molding
Molding involves shaping EPDM rubber into a predefined form using heat and pressure within a mold cavity. This process is ideal for creating complex gasket geometries with high precision and uniformity. Compression molding and injection molding are common variants. For example, compression-molded EPDM gaskets demonstrate superior dimensional stability, which is required for automotive and industrial sealing applications.
ASTM D2000 standards validate the performance of molded EPDM in extreme environmental conditions. Both solid and sponge rubber gaskets are produced through molding. Sponge rubber gaskets provide superior compressibility for softer applications, while solid gaskets offer superior tensile strength for more challenging environments.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process for producing continuous lengths of EPDM gaskets with consistent cross-sectional profiles. In this process, EPDM rubber is forced through a die to create shapes like strips, tubes, or custom profiles. Extruded EPDM gaskets are widely used in construction for window seals and weatherproofing applications.
Their flexibility and resilience against UV and ozone make them ideal for these uses. Sponge rubber gaskets are also extruded, providing excellent sealing performance in areas requiring a softer, more compressible material. Solid gaskets made through extrusion are known for their durability and strength in high-stress applications.
Die-Cutting
Die-cut EPDM gaskets are created by stamping sheet EPDM rubber into desired shapes using a precision die. This method is particularly efficient for mass-producing flat gaskets with simple or intricate designs. The die-cutting process ensures high precision and repeatability, making it perfect for large-scale production of gaskets used in industries like automotive and construction.
Solid gaskets made using die-cutting offer durability in medium-pressure applications. Sponge rubber gaskets are also die-cut, providing softer and more compressible sealing solutions for specialized uses.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to precisely cut through EPDM rubber sheets without causing thermal damage to the material. This method is appropriate for creating complex geometries and tight tolerances. Waterjet-cut EPDM gaskets are commonly used in marine seals and specialized industrial sealing solutions that require intricate designs or custom shapes. This technique allows the production of both solid and sponge rubber gaskets.
How Are Rubber EPDM Gaskets Installed?
Rubber EPDM gaskets are installed using proper surface preparation, correct alignment, and ensuring the gasket is compressed adequately to create a strong seal. The most common installation techniques include manual placement, mechanical fastening, and adhesive bonding, each suited to specific applications based on the environment and requirements.
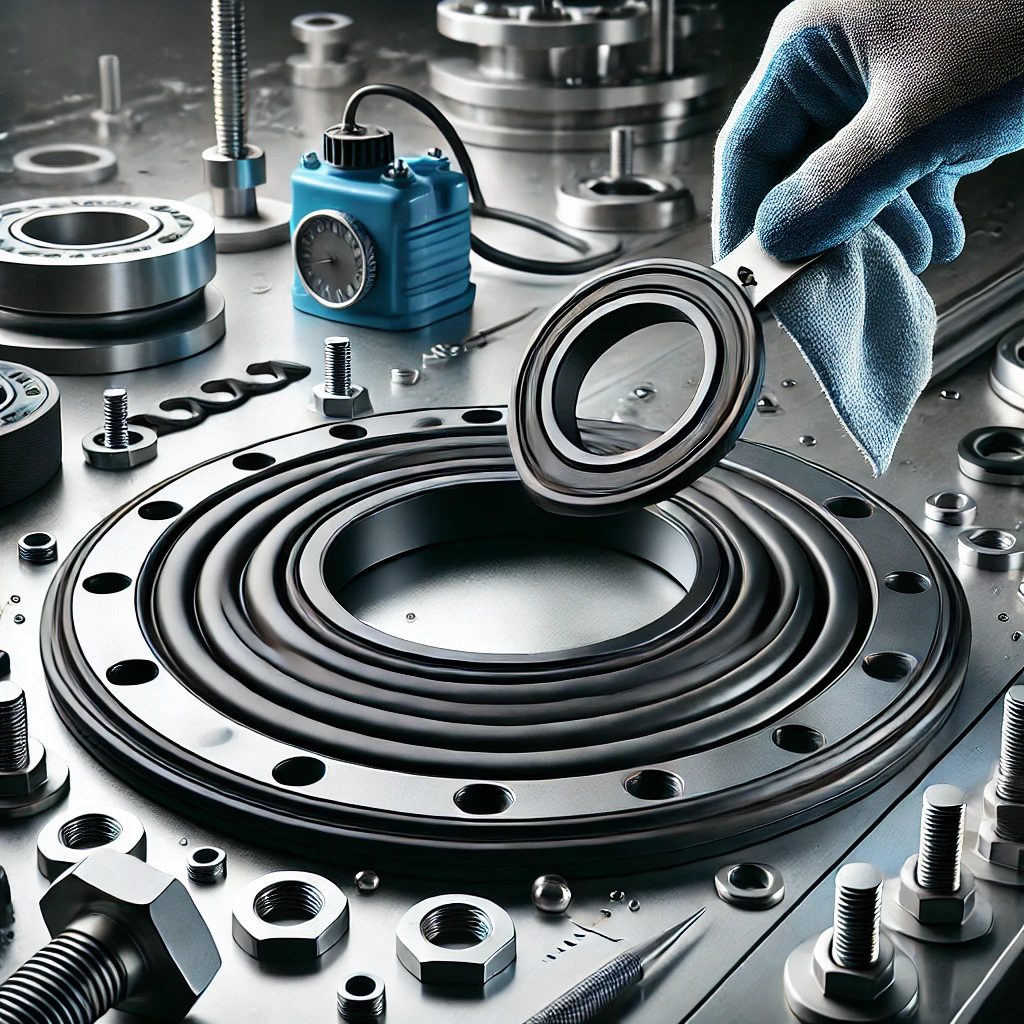

Below are the key ways EPDM gaskets can be installed:
Manual Placement
Manual placement is one of the simplest methods for installing EPDM gaskets. It is used in low-volume applications such as small HVAC systems or plumbing. In this process, the gasket is carefully positioned onto the prepared surface, ensuring that it fits within the groove or sealing area. The scientific study outlined in ASTM F104 emphasizes the importance of proper bolt-hole alignment to avoid uneven compression, which compromises the gasket’s sealing performance.
The compression area must be uniform to ensure effective sealing. A common mistake is misaligning the gasket or uneven bolt tightening, which causes leakage. Inaccurate placement leads to poor compression distribution and significantly reduces the gasket’s lifespan, especially in high-temperature or outdoor environments where EPDM’s properties, such as UV, ozone, and temperature resistance, are at play.
Mechanical Fastening
Mechanical fastening involves attaching the EPDM gasket using bolts or screws to secure it in place, used in larger industrial applications like pipelines, machinery, or automotive weatherstripping. This method ensures that the gasket is pressed evenly and maintains uniform compression throughout the installation.
ASTM F36 (which tests for gasket compression) shows that bolt-hole alignment is necessary to avoid uneven pressure across the gasket, which leads to localized deformation or leaks. Tightening bolts too quickly or unevenly damage the compression area, resulting in an inadequate seal.
Proper torque settings and following manufacturer guidelines for even pressure distribution are important for achieving leak-proof sealing. EPDM’s chemical resistance ensures it handles mechanical stresses in industrial environments while maintaining its integrity under pressure and environmental exposure.
Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding is used in applications where mechanical fastening or manual placement is not feasible, such as sensitive equipment or permanent sealing solutions. The EPDM gasket is carefully aligned and then secured with a specialized adhesive that bonds it to the surface.
Proper surface preparation, such as cleaning and priming, is compulsory to ensure the adhesive holds effectively. Failures in adhesive bonding result from inadequate surface preparation, such as the presence of dirt, oil, or old adhesive residues. This causes the bond to weaken and eventually fail.
The compression area must be distributed evenly across the gasket to avoid damaging it during installation. Missteps in choosing the wrong adhesive or failing to properly clean the surfaces significantly increase the risk of bonding failure.
What Best Practices Ensure Effective Gasket Installation?
Best practices that ensure effective gasket installation include proper surface preparation, even torque application, and periodic inspections for optimal performance. Adhering to these best practices ensures that EPDM gaskets create a reliable, leak-proof seal that withstands environmental stresses over time.
Best practices that ensure effective gasket installation are as follows:
- Surface Preparation: Effective surface preparation is an integral step in ensuring proper gasket installation. Before placing the gasket, the surfaces to be sealed must be clean and free from contaminants like dirt, oil, rust, and old gasket material. According to ASTM F104, even small residues compromise the bond between the gasket and the mating surface, leading to leaks and premature failure. According to the Gasket Handbook 2017 by the Fluid Sealing Association, failure to properly prepare surfaces reduces gasket life by up to 30%, especially in applications subject to high temperatures or chemical exposure.
- Gasket Alignment: Proper gasket alignment is important for achieving a uniform seal. Misalignment during installation leads to uneven compression, which causes localized gasket failure. Aligning the gasket carefully within the groove or sealing area and tightening bolts in a cross pattern ensures even pressure distribution and helps avoid this issue.
- Compression Control: Compression control is another important aspect of effective gasket installation. Over-compressing the gasket damages its structure, while under-compression results in insufficient sealing force. According to ASTM F36, the optimal compression range for EPDM gaskets is between 10% and 30% of the gasket’s thickness. Exceeding this range causes material deformation, leading to leaks and reduced gasket lifespan.
- Even Torque Application: Applying even torque is a fundamental practice for ensuring that the gasket is compressed uniformly across its surface. Uneven tightening of bolts or fasteners causes excessive compression in certain areas while leaving other regions insufficiently compressed, resulting in leaks. Applying torque gradually and evenly, in line with the manufacturer’s recommended torque values, is necessary to achieve optimal sealing. According to testing results under ASTM F38 standards, improper torque reduces gasket performance by up to 15%.
- Periodic Inspection: Periodic inspections and maintenance requirements are necessary to ensure that gaskets remain intact and continue to function as intended. EPDM gaskets experience wear over time due to environmental factors, mechanical stresses, or chemical exposure. Regular maintenance, including checking for signs of cracks, degradation, or leaks, helps identify potential issues before they lead to system failure. Inspections should focus on ensuring the gasket remains properly aligned and that the compression is still within the optimal range. Research by Liu J et al. 2017, titled “Service Lifetime Estimation of EPDM Rubber Based on Accelerated Aging Tests,” indicates that regular maintenance extends the life of EPDM gaskets by as much as 40%.
Common challenges that arise during gasket installation include improper surface preparation, inadequate compression, and incorrect gasket material selection for the specific application. For instance, EPDM gaskets do not provide an effective seal when used in environments with high concentrations of certain chemicals that they are not resistant to.
Over-tightening bolts in an attempt to force a tighter seal damages the gasket, leading to premature failure. A scientific study by Zaghdoudi M et al. 2023, titled “Understanding the recovery behaviour and the degradative processes of EPDM during ageing,” show that gasket failures caused by over-tightening reduce gasket efficiency by up to 20%.
What Are the Advantages of Rubber EPDM Gaskets?
The advantages of rubber EPDM gaskets include weather resistance, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. These benefits make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from automotive to industrial sealing solutions.
The advantages of rubber EPDM gaskets are as follows:
- Weather resistance: EPDM gaskets have UV resistance, resistance to ozone, and extreme temperatures. This makes them ideal for use in harsh outdoor environments. EPDM gaskets withstand temperature ranges from -40°C to +120°C without significant degradation, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh conditions.
- Cost-effective sealing solutions: Due to their durability and resistance to wear, EPDM gaskets offer a cost-effective solution, reducing the need for frequent replacements. According to Paeglis AU et al. 2004, titled “A Simple Model for Predicting Heat Aging of EPDM Rubber,” EPDM gaskets last up to 20 years in many outdoor applications, delivering significant long-term savings compared to other materials.
- Flexibility: EPDM gaskets maintain excellent flexibility, even at low temperatures. This flexibility allows them to conform to irregular surfaces and ensure a tight, leak-proof seal. It is a fundamental factor in their durability, as it helps them absorb mechanical stresses without cracking or degrading over time.
What Certifications Do Rubber EPDM Gaskets Meet?
The certifications that rubber EPDM gaskets meet include WRAS for water systems and the FDA for food-related applications. These certifications provide industrial standards for sealing in food processing and potable water systems, ensuring their suitability for a wide range of industries.
WRAS-approved EPDM gaskets comply with the regulations set by the Water Regulations Advisory Scheme, confirming their safety for use in potable water systems. They are tested to ensure they do not leach harmful substances into water and meet stringent safety standards.
Similarly, FDA-approved gaskets are important for applications in the food industry. These gaskets must comply with FDA regulations regarding materials that come into contact with food. They are manufactured to ensure they are non-toxic and do not contaminate food products.
ASTM compliance ensures that EPDM gaskets meet industrial standards for performance in areas such as chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and durability. For example, ASTM F104 sets requirements for the performance of gaskets used in sealing applications, ensuring that they meet specific mechanical and environmental criteria.
What Are the Limitations of Rubber EPDM Gaskets in Extreme Conditions?
The limitations of rubber EPDM gaskets in extreme conditions include reduced performance in oil-rich or extremely high-temperature environments. Their chemicalresistance diminishes when exposed to hydrocarbon oils, fuels, and certain solvents. In these conditions, the material degrades, swells, or loses its sealing properties, as EPDM is not compatible with oils or greases.
Research by Strouse indicates that exposure to oils reduces the mechanical properties of EPDM gaskets by as much as 50%, making them unsuitable for sealing in automotive or industrial applications involving oils and fuels.
EPDM gaskets underperform in extreme temperatures beyond their designed tolerance range. Temperatures exceeding 120°C cause the material to soften, lose its elasticity or become brittle, causing it to fail to maintain a proper seal. For instance, at temperatures above 150°C, EPDM gaskets experience significant degradation, leading to reduced temperature range tolerance and shorter service life.
This limitation makes them unsuitable for applications like high-temperature steam sealing or hot engine components, where materials like silicone or fluorocarbon rubber are more appropriate due to their higher heat resistance and material compatibility with oils and high temperatures.
Can EPDM Gaskets Be Customized for Unique Applications?
EPDM gaskets can be customized for unique applications using techniques such as die-cutting and waterjet cutting, as well as specialized material formulations. Custom gaskets are customized to fit specific design requirements, ensuring optimal performance in industrial applications with complex sealing needs.
Die-cut EPDM gaskets are created by stamping sheets of EPDM rubber into precise shapes and sizes using specialized dies. This method allows for the high-volume production of gaskets with consistent quality. It is particularly effective for applications requiring uniformity, such as HVAC systems or automotive components.
Waterjet cutting offers even greater precision. It uses high-pressure streams of water to cut EPDM into complex shapes without generating heat that could affect the material’s properties. This technique is ideal for prototypes or low-volume production runs where flexibility and accuracy are paramount, such as in aerospace or specialized machinery.
EPDM formulations are customized to improve specific properties, such as increased chemical resistance or improved temperature tolerance, broadening their application scope. For instance, industries requiring gaskets resistant to aggressive chemicals or extreme weather benefit from EPDM blends tailored to these conditions.
What Are the Benefits of Customizing EPDM Gaskets?
The benefits of customizing EPDM gaskets are precision fit, improved performance, and application-specific design. It also ensures that gaskets meet specific thickness options, providing a perfect seal for unique industrial requirements.
Waterjet customization allows for complex designs and tight tolerances, making it ideal for prototypes and low-volume applications. On the other hand, die-cut EPDM gaskets are cost-effective for high-volume production that maintains consistent quality. By customizing gaskets to particular needs, manufacturers optimize their performance, reduce waste, and extend the lifespan of application-specific gaskets.
What Maintenance Practices Ensure Long-Lasting EPDM Gaskets?
The maintenance practices that ensure long-lasting EPDM gaskets include periodic inspections, routine cleaning, and proactive replacement of worn components. Regular periodic inspections help identify signs of wear, such as cracks or deformation, ensuring timely intervention before gasket failure occurs.
Cleaning protocols using non-abrasive methods prevent the buildup of dirt, grease, or chemicals that compromise the gasket’s performance. EPDM’s natural aging resistance to UV rays and ozone further minimizes degradation, but proactive replacement of damaged or excessively worn gaskets ensures consistent sealing efficiency. Following these maintenance requirements extends the lifespan of EPDM gaskets, reducing downtime and maintaining optimal performance in challenging environments.
When Should EPDM Gaskets Be Avoided?
EPDM gaskets should be avoided in hydrocarbon oils or applications exceeding 150°C. Their lack of hydrocarbon resistance makes them unfit for sealing applications involving fuels, oils, or solvents. These substances cause the material to swell, degrade, or lose its sealing properties.
EPDM gaskets are limited in their ability to withstand extremely high temperatures. They perform well within a temperature range of -40°C to +120°C, but applications beyond 150°C lead to softening, cracking, or complete failure of the material.
For such conditions, alternative materials like fluorocarbon (Viton) or silicone rubber are better suited. High-temperature gaskets made from these materials offer superior chemical and temperature resistance, making them ideal for use in environments with hydrocarbons or temperatures exceeding EPDM’s limits. Understanding these material limitations ensures the selection of the most appropriate gasket for each specific application.
Where can EPDM Gaskets be Bought?
EPDM gaskets can be bought in specialized industrial supply stores, online marketplaces, and directly from EPDM Gaskets manufacturers offering custom solutions. Many suppliers offer a wide range of EPDM gaskets to meet diverse industrial needs, including standard and custom configurations. For reliable and high-quality options, explore Rubber Gaskets by RubberXperts. Their products are designed to meet stringent industry standards. The suppliers offer expert guidance on selecting the right gasket for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
What Innovations Are Enhancing EPDM Gasket Applications?
Innovations enhancing EPDM gasket applications include advancements in material formulations, such as peroxide curing, UL 94 flame retardancy, and improved chemical resistance.
Peroxide-cured EPDM offers superior heat resistance and mechanical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature and high-stress environments. Achieving UL 94 compliance for flame retardancy expands the use of EPDM gaskets in industries like electronics and aerospace, where fire safety is necessary.
These advanced formulations improve durability and performance and enable EPDM gaskets to meet stringent industry requirements. They ensure reliability in high-performance gaskets used in automotive, construction, and industrial sealing applications. Such innovations underscore EPDM’s adaptability to evolving demands in specialized industries, further solidifying its role as a versatile and dependable material.
How Can EPDM Gaskets Support Sustainability Goals?
EPDM gaskets can support sustainability goals through eco-friendly manufacturing processes and recyclability, making them a cost-effective choice for green projects.
The production of eco-friendly EPDM gaskets involves using renewable resources and reducing the carbon footprint during the manufacturing process, which significantly contributes to environmental sustainability. EPDM gaskets are made from recyclable materials, meaning they are repurposed at the end of their life cycle, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Beyond environmental considerations, EPDM gaskets offer sustainable sealing solutions that are durable and require less frequent replacement, further lowering resource consumption over time. Their long-lasting performance in demanding applications not only reduces the need for replacements but also helps minimize the overall environmental impact.
By choosing recyclable materials and employing energy-efficient production methods, EPDM gaskets offer a cost-effective and environmentally responsible choice for industries aiming to meet sustainability goals without compromising on performance.





